Milo Newman, PhD candidate in human geography, introduces his project on creativity and extinction. Milo’s research is funded through the AHRC South West and Wales Doctoral Training Partnership.
Looking at your hearts, suspended in their jar, I try and imagine the two of you still alive. I know that if you were anything like your closest living kin, you would have bonded for life. You lived a long time, and it would have been a relationship that had gathered and deepened over years. By the time you came together this final time, the congregations that were so important to your kind were already a thing of the past. Perhaps you were aware of how empty your world had become. Although you were alone on that low rock, it could be that you were accompanied by the memory of the multitude that had once been. By this point it was already too late. There were too few of you to recover what had been lost. Even so, maybe you would have nodded to each other and tried to make the best of it. Maybe you would have started showing off, just as those before you had always done; turning your heads from side to side so the bright white around your eye would have caught the light. Maybe then, with an exuberance tinged with grief, you would have thrown your heads back and let out an ecstatic cry; the vivid yellow inside your mouths shining like a beacon, mimicking the sun.
Catastrophic anthropogenically-driven biodiversity loss is a defining problem of our time, with hundreds of extinctions observed every year, and many more occurring unnoticed. Reacting to the scale of this issue, extinction studies researchers have called for new interdisciplinary responses interrogating what extinction means, why it matters, and how it is narrated.
‘Mourning Auks’ is an innovative practice-led project examining how artful geographic methods and outcomes can contribute to these vital questions. Over the next four years I plan to explore what novel and affective modes of engaging with anthropogenically-driven species loss can be generated through creative articulations of the emotional dimensions of extinction, and how these can be communicated in public artistic and museum contexts.
In extinction studies, extinction is understood not as a singular, generic concept, but as something that exists through multiple specificities relatable to the diversity of lifeworlds being lost. This is generally explored via case studies, which employ critically-driven creative-academic storytelling to express the biological, cultural and temporal particularities of species, their unique phenomenal worlds, and the significance of extinction within multispecies entanglements. This narrative-based approach provides a form of witnessing that is attentive to others in the face of irreparable loss, that counters human exceptionalism, and creates new ethical and cultural modes that help to resist the destructive legacies of anthropogenically-driven extinction more broadly.
Unexplored potential exists for artistic methods to undertake and communicate these extinction-orientated case studies. Through a case study on the now extinct great auk, my practice-led project will explore and analyse ways of engaging broader audiences with this field. It aims to expand the affective reach of these essential attempts to re-articulate contemporary species loss, and its ethical and socio-cultural imperative.
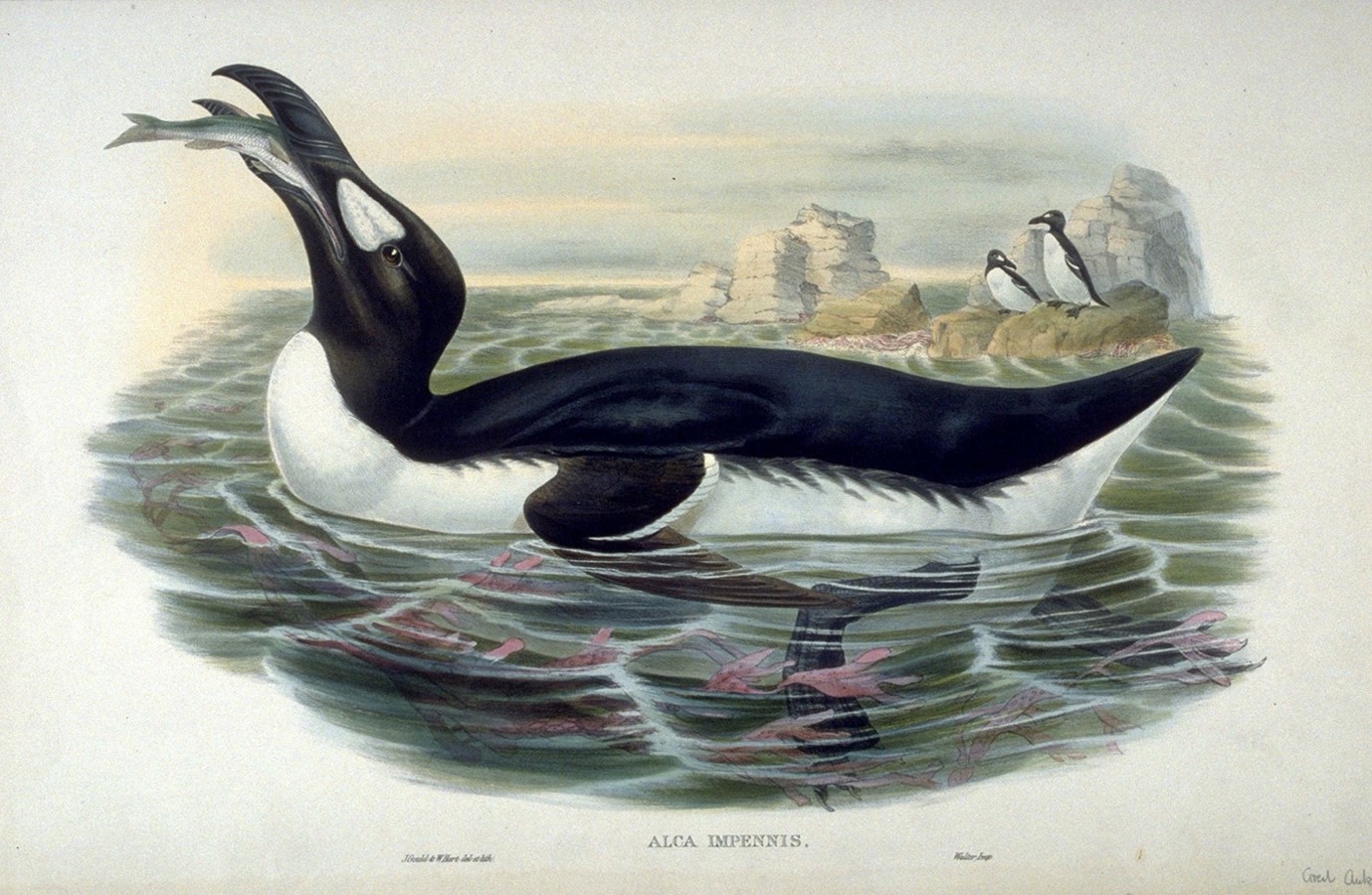

The great auk was a flightless seabird that was once found in the cold coastal waters of the North Atlantic. These birds nested in huge social colonies on isolated islands, which they returned to every year. These remote skerries provided protection from terrestrial predators. However, they became increasingly vulnerable after technological advances in ocean-going vessels brought European sailors into close proximity to these breeding colonies, which they ruthlessly exploited for food on trans-Atlantic voyages.
My research will begin with analysis of the ‘Garefowl books’, a substantial, underexploited resource held in the Cambridge University Library collections. These manuscript diaries, kept by the Victorian ornithologist and egg collector John Wolley, record interviews with witnesses who were amongst the last to see the auks alive, and who took part in the final hunting parties to their breeding places. Close reading of this material will inform studio-based experimentation utilising artistic methods drawn from archival impulses in contemporary art (see the works of John Akomfrah and Tacita Dean, amongst many others). Following on from Brian Massumi’s 2014 book What Animals Teach us About Politics such ‘playful’ creative practices can be seen as animal in origin, and provide a continuum with animal life (see Merle Patchett’s Archiving). In this context, these textual encounters with the auk’s disappearance offer the means of both interrogating the socio-cultural practices that drove their extinction, and of generating sympathetic multispecies re-alignments.
I also plan to draw the narratives surrounding the auks’ disappearance into emotional geographic frames. These examine spatialisations of emotion in relation to landscape, including those relating to death, such as mourning and grief. Study here is mostly restricted to human contexts, and my project aims to develop this to explore the affective geographies of sites of extinction-driven absence.
In recent re-interpretations, avian philopatry has been re-conceptualised as other-than-human ‘storying-of-place’ (see Thom van Dooren’s excellent book Flight Ways). Hypothesising this for great auks gives their breeding sites potency as places, not just because they were invested with history and meaning for the auks, but because these became the traumatic sites of their extinction. In this context, I plan to undertake fieldwork at some of the auks’ historical breeding colonies, and at those of their closest living relatives. Here, imaginative curiosity towards these species’ remote, liminal, and aquatic geographies will inform a creative enlivening of the great auks’ historical lifeworld, providing the basis for further artistic experimentation centred on site-specific place-making exercises. These will attend to how landscapes are matters ‘of [other-than-human] biographies, attachments and exiles’ in which ‘absence, loss and haunting’ abound (Wylie, 2007: 10), and will survey the more-than-representational emotional aspects of extinction.
You can follow Milo on twitter @_milonewman and see more of his work at www.milonewman.com

